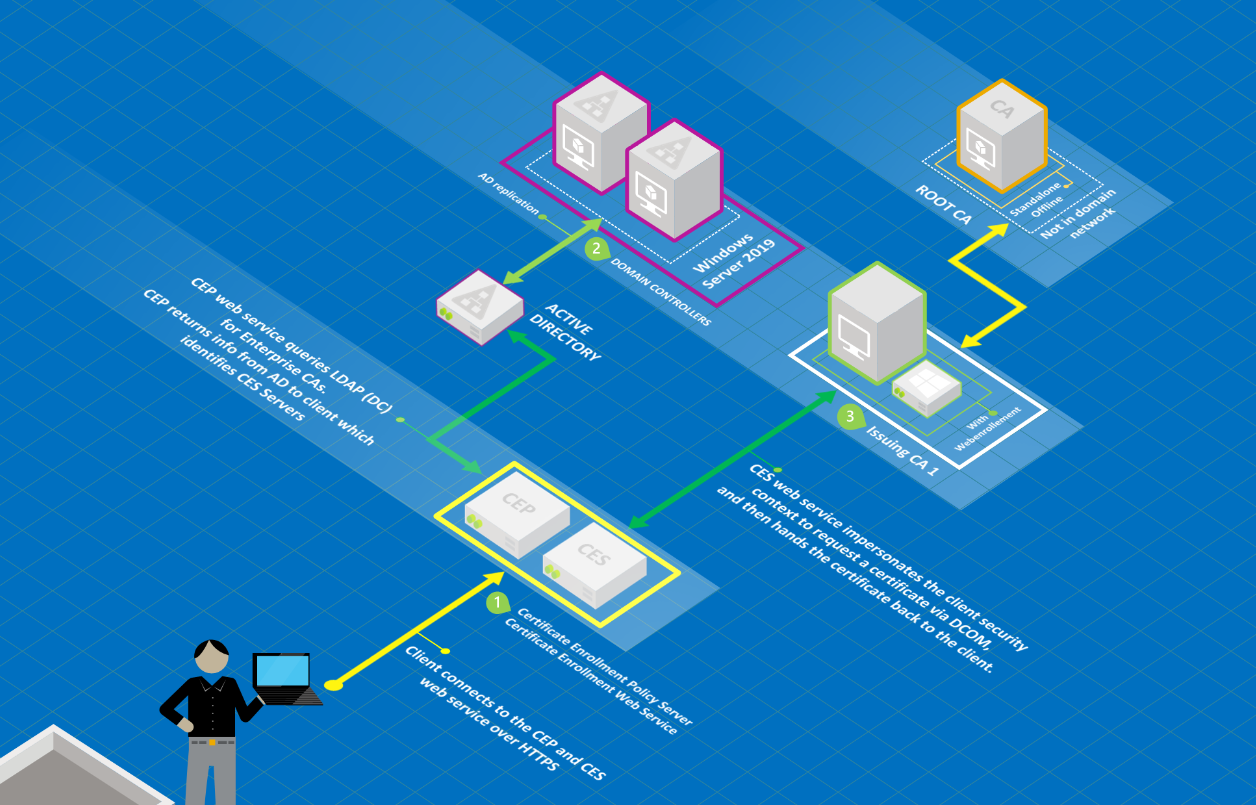
This article provides step-by-step instructions to implement the Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service (CEP) and Certificate Enrollment Web Service (CES) on a custom port other than 443 for certificate key-based renewal to take advantage of the automatic renewal feature of CEP and CES.
This article also explains how CEP and CES works and provides setup guidelines.
The workflow that's included in this article applies to a specific scenario. The same workflow may not work for a different situation. However, the principles remain the same.
Disclaimer: This setup is created for a specific requirement in which you do not want to use port 443 for the default HTTPS communication for CEP and CES servers. Although this setup is possible, it has limited supportability. Customer Services and Support can best assist you if you follow this guide carefully using minimal deviation from the provided web server configuration.
For this example, the instructions are based on an environment that uses the following configuration:

This section provides the steps to configure the initial enrollment.
You can also configure any user service account, MSA, or GMSA for CES to work.
As a prerequisite, you must configure CEP and CES on a server by using username and password authentication.
You can duplicate an existing computer template, and configure the following settings of the template:
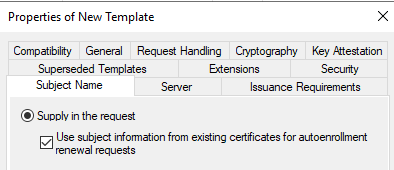
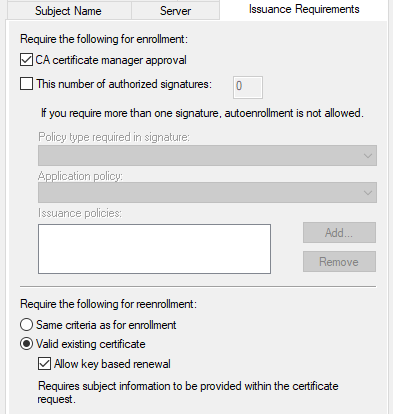
Make sure the compatibility settings on the template is set to Windows Server 2012 R2 as there is a known issue in which the templates are not visible if the compatibility is set to Windows Server 2016 or later version. For more informaiton, see Cannot select Windows Server 2016 CA-compatible certificate templates from Windows Server 2016 or later-based CAs or CEP servers.
To install the CEPCES01 instance, use either of the following methods.
Method 1
See the following articles for step-by-step guidance to enable CEP and CES for username and password authentication:
Make sure that you do not select the “Enable Key-Based Renewal” option if you configure both CEP and CES instances of username and password authentication.
Method 2
You can use the following PowerShell cmdlets to install the CEP and CES instances:
Import-Module ServerManager Add-WindowsFeature Adcs-Enroll-Web-Pol Add-WindowsFeature Adcs-Enroll-Web-Svc Install-AdcsEnrollmentPolicyWebService -AuthenticationType Username -SSLCertThumbprint "sslCertThumbPrint" This command installs the Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service (CEP) by specifying that a username and password is used for authentication.
In this command, SSLCertThumbPrint> is the thumbprint of the certificate that will be used to bind IIS.
Install-AdcsEnrollmentWebService -ApplicationPoolIdentity -CAConfig "CA1.contoso.com\contoso-CA1-CA" -SSLCertThumbprint "sslCertThumbPrint" -AuthenticationType Username This command installs the Certificate Enrollment Web Service (CES) to use the certification authority for a computer name of CA1.contoso.com and a CA common name of contoso-CA1-CA. The identity of the CES is specified as the default application pool identity. The authentication type is username. SSLCertThumbPrint is the thumbprint of the certificate that will be used to bind IIS.
 Services Manager console." />
Services Manager console." />
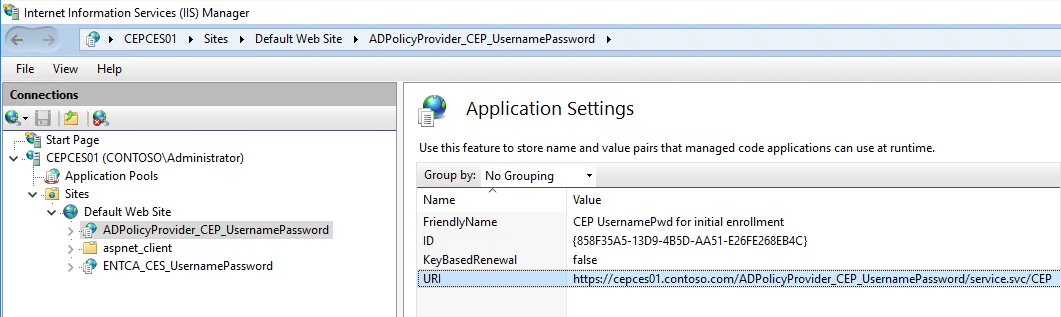
After a successful installation, you expect to see the following display in the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager console.
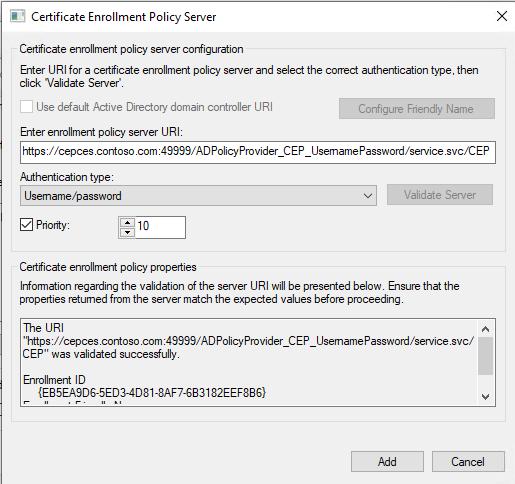
Under Default Web Site, select ADPolicyProvider_CEP_UsernamePassword, and then open Application Settings. Note the ID and the URI.
You can add a Friendly Name for management.
Run the following command in PowerShell:
Install-AdcsEnrollmentPolicyWebService -AuthenticationType Certificate -SSLCertThumbprint "sslCertThumbPrint" -KeyBasedRenewal This command installs the Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service (CEP) and specifies that a certificate is used for authentication.
In this command, is the thumbprint of the certificate that will be used to bind IIS.
Key-based renewal lets certificate clients renew their certificates by using the key of their existing certificate for authentication. When in key-based renewal mode, the service will return only certificate templates that are set for key-based renewal.
Install-AdcsEnrollmentWebService -CAConfig "CA1.contoso.com\contoso-CA1-CA" -SSLCertThumbprint "sslCertThumbPrint" -AuthenticationType Certificate -ServiceAccountName "Contoso\cepcessvc" -ServiceAccountPassword (read-host "Set user password" -assecurestring) -RenewalOnly -AllowKeyBasedRenewal This command installs the Certificate Enrollment Web Service (CES) to use the certification authority for a computer name of CA1.contoso.com and a CA common name of contoso-CA1-CA.
In this command, the identity of the Certificate Enrollment Web Service is specified as the cepcessvc service account. The authentication type is certificate. SSLCertThumbPrint is the thumbprint of the certificate that will be used to bind IIS.
The RenewalOnly cmdlet lets CES run in renewal only mode. The AllowKeyBasedRenewal cmdlet also specifies that the CES will accept key based renewal requests for the enrollment server. These are valid client certificates for authentication that do not directly map to a security principal.
The service account must be part of IIS_IUSRS group on the server.
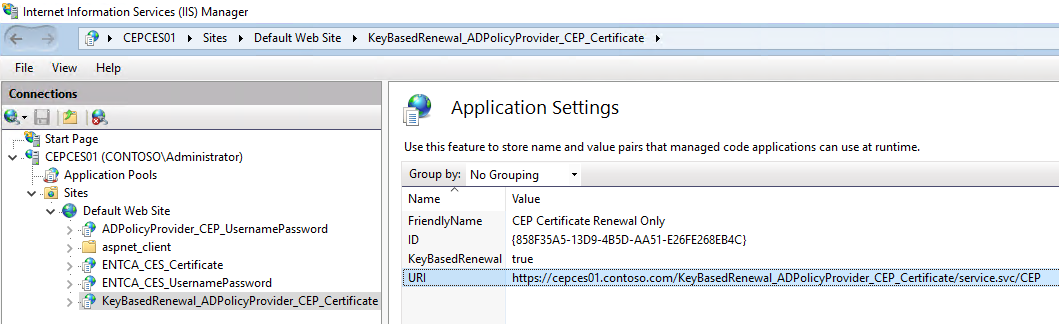
After a successful installation, you expect to see the following display in the IIS Manager console.
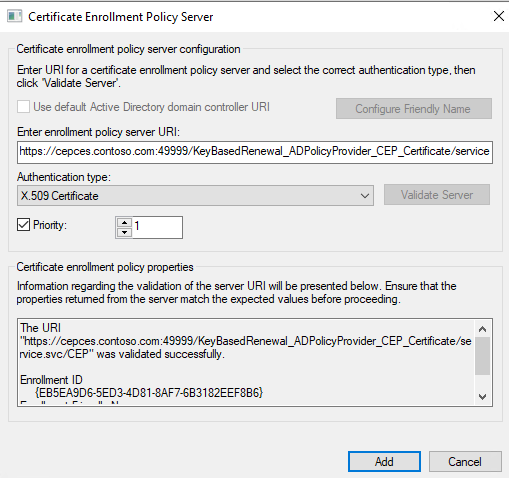
Select KeyBasedRenewal_ADPolicyProvider_CEP_Certificate under Default Web Site and open Application Settings. Take a note of the ID and the URI. You can add a Friendly Name for management.
If the instance is installed on a new server double check the ID to make sure that the ID is the same one that was generated in the CEPCES01 instance. You can copy and paste the value directly if it is different.
To be able to enroll the certificate on behalf of the functionality of CEP and CES, you have to configure the workgroup’s computer account in Active Directory and then configure constrained delegation on the service account.
This account will be used for authentication towards key-based renewal and the “Publish to Active Directory” option on the certificate template.
You do not have to domain join the client machine. This account comes into picture while doing certificate based authentication in KBR for dsmapper service.

Run the following PowerShell command to enable constrained delegation (S4U2Self or any authentication protocol):
Get-ADUser -Identity cepcessvc | Set-ADAccountControl -TrustedToAuthForDelegation $True Set-ADUser -Identity cepcessvc -Add @ <'msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo'=@('HOST/CA1.contoso.com','RPCSS/CA1.contoso.com')>In this command, is the service account, and is the Certification Authority.
We are not enabling the RENEWALONBEHALOF flag on the CA in this configuration because we are using constrained delegation to do the same job for us. This lets us to avoid adding the permission for the service account to the CA’s security.
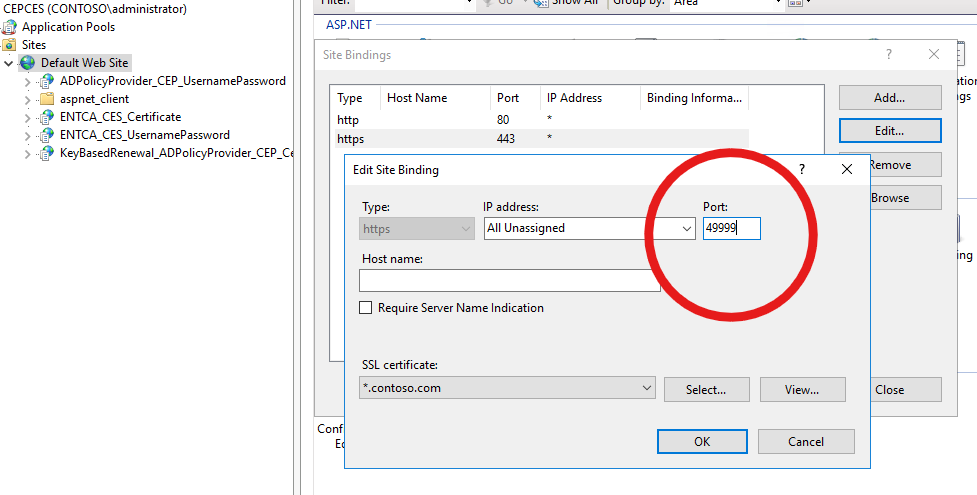
140https://cepces.contoso.com:49999/ENTCA_CES_UsernamePassword/service.svc/CES0 181https://cepces.contoso.com:49999/ENTCA_CES_Certificate/service.svc/CES1 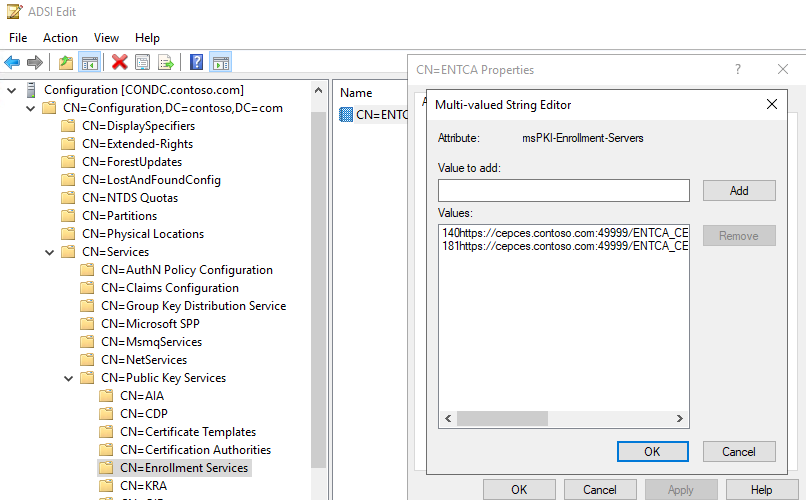
On the client computer, set up the Enrollment policies and Auto-Enrollment policy. To do this, follow these steps:
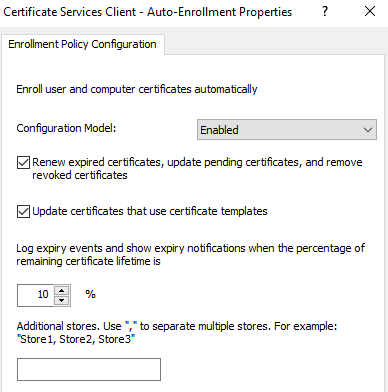
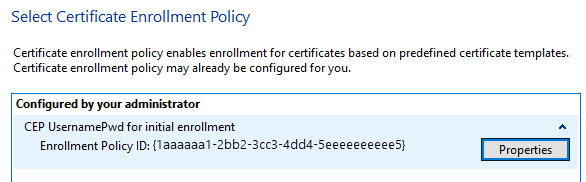 Select the KBR template and enroll the certificate.
Select the KBR template and enroll the certificate. 
Make sure that the priority value of the key-based renewal enrollment policy is lower than the priority of the Username Password enrollment policy priority. The first preference is given to the lowest priority.
To make sure that Auto-Renewal is working, verify that manual renewal works by renewing the certificate with the same key using mmc. Also, you should be prompted to select a certificate while renewing. You can choose the certificate we enrolled earlier. The prompt is expected.
Open the computer personal certificate store, and add the “archived certificates” view. To do this, add the local computer account snap-in to mmc.exe, highlight Certificates (Local Computer) by clicking on it, click view from the action tab at the right or the top of mmc, click view options, select Archived certificates, and then click OK.
Run the following command:
certreq -machine -q -enroll -cert renew 
Advance the time and date on the client machine into the renewal time of the certificate template.
For example, the certificate template has a 2-day validity setting and an 8-hour renewal setting configured. The example certificate was issued at 4:00 A.M. on 18th day of the month, expires at 4:00 A.M. on the 20th. The Auto-Enrollment engine is triggered on restart and at every 8-hour interval (approximately).
Therefore, if you advance the time to 8:10 P.M. on the 19th since our renewal window was set to 8-hour on the template, running Certutil -pulse (to trigger the AE engine) enrolls the certificate for you.
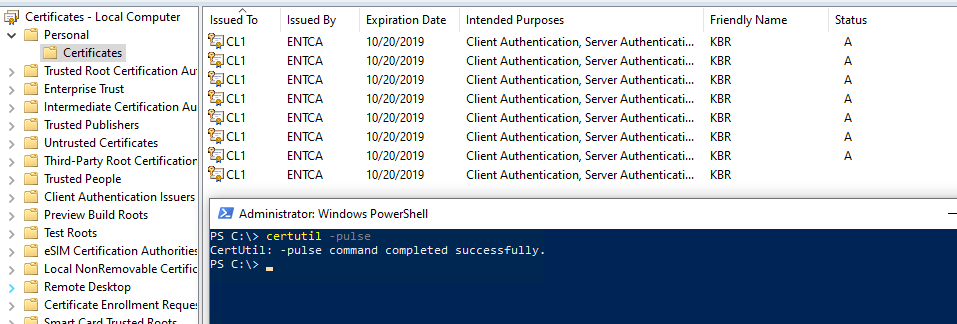
After the test finishes, revert the time setting to the original value, and then restart the client computer.
The previous screenshot is an example to demonstrate that the Auto-Enrollment engine works as expected because the CA date is still set to the 18th. Therefore, it continues to issue certificates. In a real-life situation, this large amount of renewals will not occur.