
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) cables play an essential role in the control of fans and pumps in electronic devices. These cables, thanks to their unique design, enable devices to adjust their cooling speed dynamically by regulating the voltage supplied to the fan motor. This results in more accurate cooling responses to temperature changes inside the device, leading to efficient thermal management and reduced noise levels.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Pulse Width Modulation Cable |
| What it Does | Carries a signal to control fan speed |
| How it Works | Uses a series of on-off pulses to regulate power delivered to a fan |
| Benefits | – Precise control over fan speeds |
| Connection | Typically a 4-pin connector |
| Plugs into | A 4-pin header on the motherboard labeled “CPU_FAN” or “SYS_FAN” |
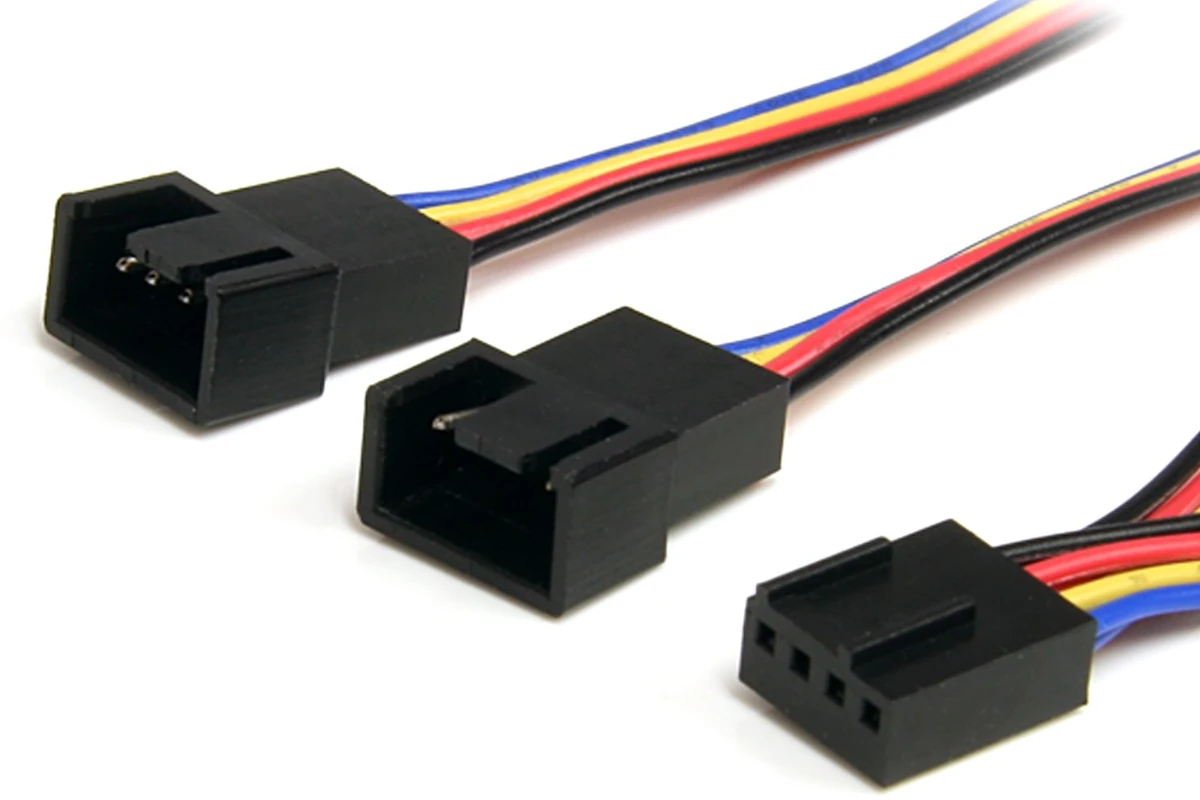
PWM cables often include a 4-pin connector, which differs from the traditional 3-pin fan connector by an additional pin for controlling fan speeds. These cables should ideally be connected to the motherboard’s 4-pin headers, which are typically labeled with names like “CPU_FAN” or “SYS_FAN.” It is crucial for the devices’ thermal performance that the PWM cables are correctly plugged into the right headers on the motherboard, an activity that can be done by following the motherboard’s manual or seeking advice from online forums if the labeling on the motherboard is unclear.
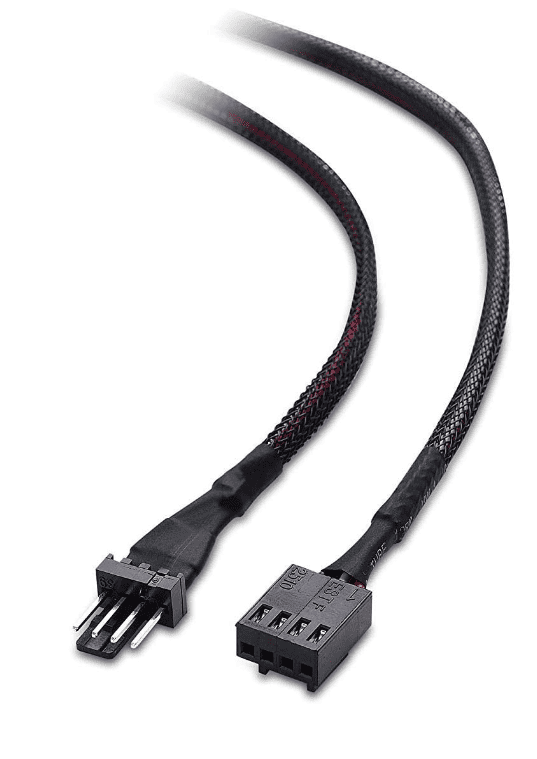
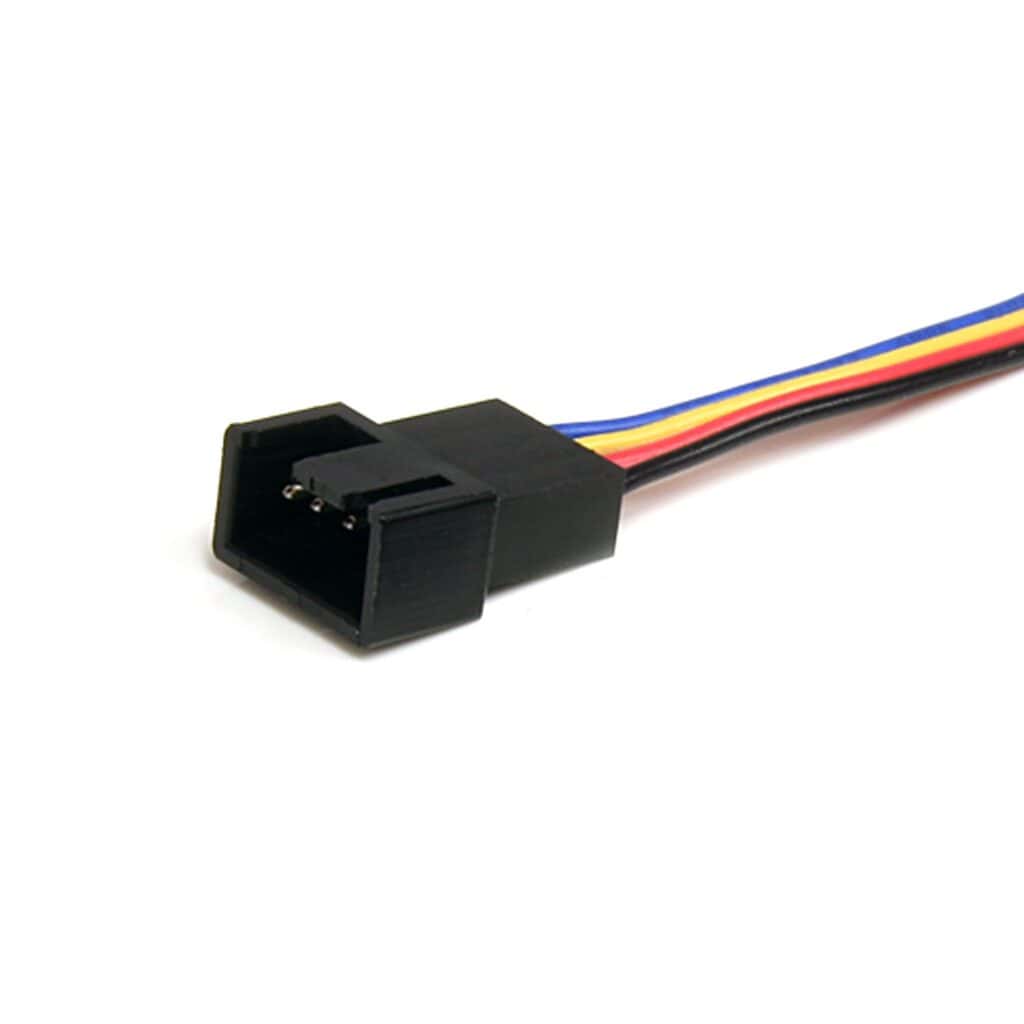

There are two main types of fans used in computers: PWM fans and DC (or regular) fans. PWM fans have 4-pin connectors and allow for more accurate speed control; connect these to 4-pin headers on your motherboard. Ensure the tab on the connector aligns with the guide on the motherboard header to avoid damage. DC fans use a 3-pin connector and can be connected to either 3-pin or 4-pin headers, but with less precise control.
Balancing cooling performance with a quiet environment involves managing fan speeds. Most motherboards come with a Smart Fan Mode in the BIOS settings that automatically adjusts the fan speeds based on temperature readings. For manual control, fan controller software or hardware can grant you command over individual fans. When connecting multiple fans, splitters, Y-splitters, or hubs can be employed but consider the total amperage to prevent overloading the header. Extensive use of these might necessitate extensions or additional power sources to manage the load effectively.